This describes an older ST-Developer release (2017). You can find the details for the latest release here
Overview
Version 17 of the STEP Tools® software stack of libraries and tools is now spread across several packages. The Core SDK package contains software needed for all types of data, with separate Project Packs that covers applications based on STEP CAD, IFC BIM, or Digital Thread applications.
We simplified STEP applications with a single EXPRESS class library that covers all APs. The STEP faceter is stronger and faster with easy creation of AP242 tesselated models or XML for lightweight viewing. We have new APIs for geometric tolerances with a full range of functions for working with datums, common datums, datum modifiers, and tolerance modifiers. A new STEP checker and browser makes it easy to investigate data sets on any platform.
IFC applications get a boost with the new IFC Faceter, an IFC checker and browser, and improvements in automatic migration from older ifc2x3 data.
Finally there is a new CAD Math Library for easy work with transforms, vectors, points, meshes, unit conversions and other common math. There are also many general updates, such as support for the new 2016 edition of the Part 21 file format. The migration guide has detailed information about API changes in the libraries.
STEP Check and Browse
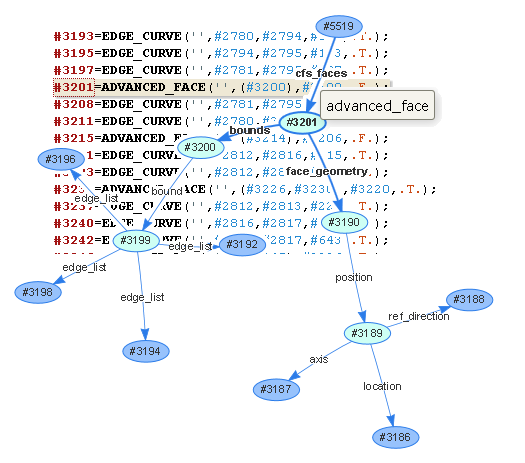
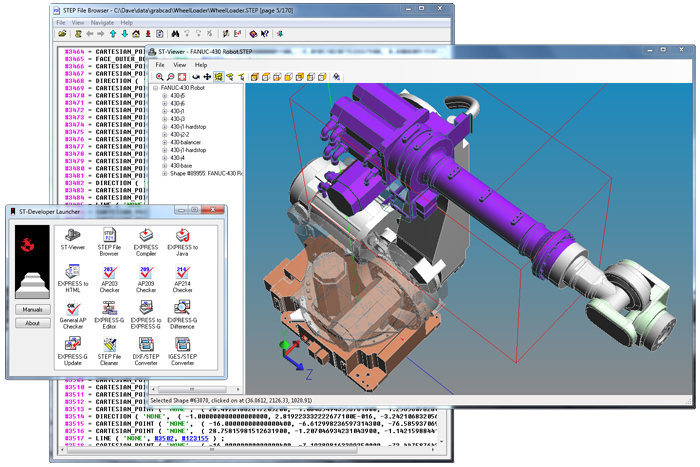
The new stpcheck combines checking and browsing in a single tool. It can analyze STEP file contents and print reports like previous AP checkers, but now you can move beyond batch operation to interactive viewing using the built-in web server.
This tool is integrated into the Windows file explorer, so you can just right click on a file and select "Check STEP File" from the pop-up menu. It will start a local web-server and launch your browser. From there, you can build instance graphs, follow links forwards and backwards between objects, see the range of types in the file, look at the EXPRESS schema definitions, and browse STEP files that are hundreds of megabytes in size!
The stpcheck tool fully recognizes all common STEP schemas (AP242, AP214, AP203, STEP-NC) and can read and recognize the common parts of unusual STEP files. Since the user interface is just any web browser, the tool works on all supported platforms!
Geometric Tolerances
STEP CAD models now hold geometric tolerances associated with faces. AP242 has updated tolerance definitions with many more options and extra parameters. The latest libraries have API calls to easily create and navigate tolerances. The API has functions to create them, find their type, get and put modifiers, datums, and extra parameters. This is much simpler than trying to use the raw C++ classes for each type.
The core of the API uses single call to create any type of tolerance, as well as some functions to test whether the tolerance can hold different types of extra settings. The previous approach was not practical because it required raw C++ classes for each of the 259 possible AND/OR combinations, plus code in your application to pick between them. Key functions for creating and testing tolerances:
- stix_make_tolerance()
- stix_tol_geometric_type()
- stix_tol_type()
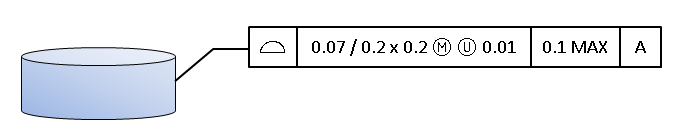
Surface Profile with All Possible Extra Parameters
The extra parameters, like per area basis or unequal displacement, each have functions to get and set values. Key functions for getting and setting the extra parameters are:
- stix_tol_get/put_area_type()
- stix_tol_get/put_displacement()
- stix_tol_get/put_maximum_upper_tolerance()
- stix_tol_get/put_second_unit_size()
- stix_tol_get/put_unit_size()
There are also functions for traversing the set of tolerance modifiers, adding or removing modifiers, and managing the values. These functions also understand the old ap214-style modifier and will automatically translate MMC and LMC into a simple modifier enum. Some key functions for modifiers are:
We put in much work on handling datums, common datums, and datum modifiers. The functions easily loop over all of the datums associated with a tolerance. Other functions loop over the modifiers of a datum. When creating data, the functions use the latest AP242 definitions, but they also understand older AP214 style references, so you do not need to worry about the specifics. Some of the datum functions are:
- stix_tol_add_datum()
- stix_tol_add_common_datum()
- stix_tol_add_datum_modifier()
- stix_tol_get_datum()
- stix_tol_get_datum_modifier()
- stix_tol_remove_datum()
- stix_tol_remove_datum_modifier()
Other STEP Enhancements
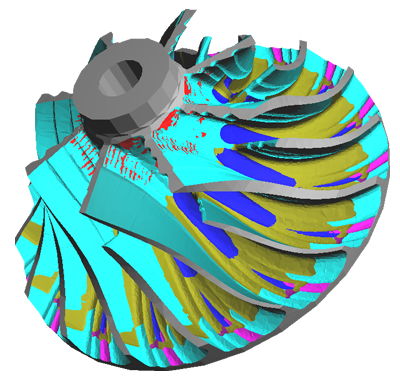
Mesh created by STEP-NC Simulator
We continue to improve the STEP Faceter library with better AP242 handling, more geometry, and faster speed. We also have the latest definitions in our STEP CAD and STEP Manufacturing AP libraries!
- STEP Faceter Library
[change log]
- New STEP to STL Sample Program for using the STEP Faceter library in Additive Manufacturing applications. We also open-sourced the export_product_asm tool and have expanded it into a more extensive STEP to STL or WebGL program on our GitHub projects.
- Can save meshes as AP242 tesselated models for use in downstream simulation or other systems. The AP242 models preserve faces and can have colors. There are also new functions for saving arbitrary sets of facets, such as portions of faces, for debugging or other purposes.
- The facet data structure still holds normals for each vertex, but no longer stores a normal for the entire triangle. The vertex normals have been renamed from "vert_normals" to just "normals", and the StixMeshfactSet::getFacetNormal() function computes the triangle normal.
- Added a face property mechanism for attaching additional information to faces.
- New support for reading and handling AP242 tessellated_surface_sets and tessellated_faces. Now reading and processing bounded_curve AND surface_curve used to trim curve_bounded_surface instances.
- New API functions for getting the area of surfaces and for 2D Delaunay mesh generation.
- Stability improvements in many areas: handling unfacetible faces, NULL faces, vertices or facets, bad data in AP242 tesselated models, validating senses in topology
- Fixed mesh topology when faceting geometry such as cylinder trimmed by two complete circles. A seam is now added correctly.
- Expanded handling of trimmed periodic surfaces, particularly where wrap-around occurrs inside the trimmed area, such as a torus trimmed by complete circles.
- Continuous improvements in speed, topology handling, and small or degenerate faces. Better topology validation and more predictable NURBS curve parameterization. Fixed a NURBS reparameterize issue that was causing failures with surfaces of revolved NURBS curves.
- STEP data with a geometric uncertainty of zero (infinitely precise) is now handled sensibly.
- STEP Merged APs Library
- AP242, AP238, AP214, and AP203 in a single application!
- Simplified complex instance combinations for handling geometric tolerances
- AP242e1 support, plus added AP242e2 Point Cloud definitions for shape representations defined by 3D scan data.
- Added support for the AP232 technical data packaging schema.
- Now recognizing the circa 2005 CAX-IF construction history (SMCH) testing schema "CCD_CLA_GVP_AST_ASD" as ap203e2, and files with "AUTOMOTIVE_DESIGN_CC2" as AP214. These schema names made it into some commercial tools.
- Added complex instance combinations to support tesselated display PMI now being created by Catia.
- Added definitions to support the proposed CAX-IF Minimal Presentation PMI.
- Fixed "name" attributes incorrectly redeclared as derived in characterized_representation and kinematic_pair entities. These definitions inherit two different name attributes. The wrong ones were marked as redeclared, so a "*" was not in the proper place in P21 files. This also affected any subtypes or complex instance combination with these types.
- STIX AP Helper Library
[change log]
- Simplified API for geometric tolerances described above.
- New helper functions for querying geometric uncertainties attached to STEP solid models.
IFC BIM Faceter
We are adding a new IFC Faceter library that makes viewable meshes from IFC data, just like our STEP Faceter does for STEP. We have also improved the IFC BIM library to move between IFC2x3 and IFC4 with greater ease!
We are also working on a new .NET API for building IFC tools. It has the same power as our C++ API, but can be used directly from C# or Visual Basic. Contact us if you are a customer who wants early access for testing!
- IFC Faceter Library
[change log]
- This is a developer preview of our IFC Faceter Library. We anticipate many more iterations, so contact is if you are interested so that we can keep you supplied with the latest features!
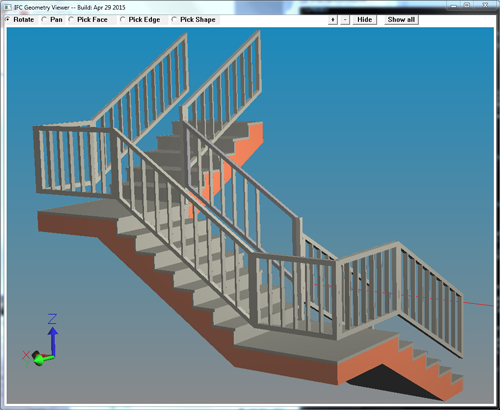
- The faceter handles IFC data with extruded solids that have profiles made up of circles, trimmed_curves, composite_curves, polylines, or lines. It handles shell-based surface models and solids that are faceted_breps with triangle or quad facets. The faceter also resolves color styles that appear in the IFC data.
- We include a very simple IFC geometry viewer (ifcview.exe) as a test harness to display mesh data. Call it from the command line with your filename.
- IFC BIM Library
[change log]
- Added automatic migration support for types that have extra attributes in IFC4 but no other significant structural changes. The extra fields are present when writing IFC4 but not used when writing the file as IFC2x3 or IFC2x2. There are no longer warnings about missing fields when reading these types in IFC2x3 data. See the release notes for a full list of types that have been enhanced.
- Add aliases for reading the IfcBezierCurve, IfcRationalBezierCurve, Ifc2DCompositeCurve types that were removed in IFC4. These are simple subtypes with no extra fields, so just handle them as instances of the supertype.
- Corrected case-sensitive comparison issue that caused schema initialization issues on Linux, AIX, Solaris, and HPUX.
- IfcSurfaceStyleShading gained an optional attribute moved from a subtyle in ifc4_add1. Supressing warnings about the extra attribute when reading or writing as IFC 2x3 data.
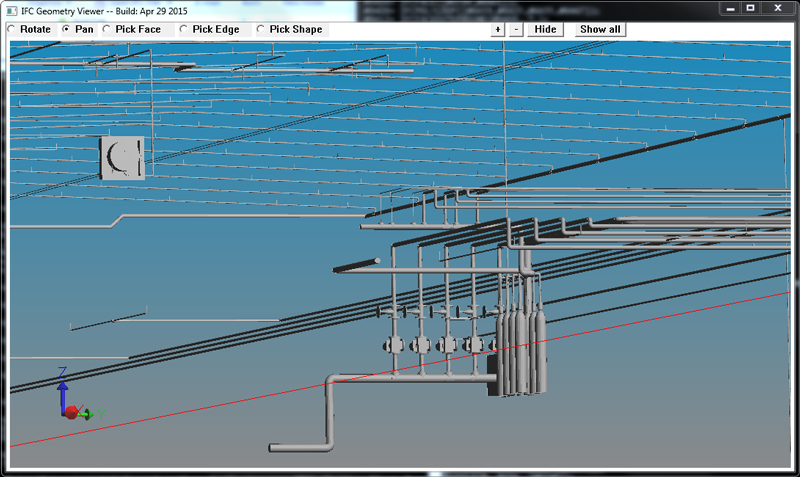
IFC Check and Browse
The new ifccheck is a combined checking and browsing tool for IFC files. Like stpcheck, it can analyze IFC file contents and print reports and do interactive viewing using the built-in web server.
This tool is integrated into the Windows file explorer, so you can just right click on a file and select "Check IFC File" from the pop-up menu. It will start a local web-server and launch your browser. From there, you can build instance graphs, follow links forwards and backwards between objects, see the range of types in the file, look at the EXPRESS schema definitions, and browse very large IFC files!
Math Library
The ROSE Math Library is a new addition to our software stack that contains functions for working with vectors, transforms, meshes, unit conversions, and other operations common to engineering data. There is nothing in here that is specific to an information model (STEP, IFC, CIS/2, DSTV, etc) so it can be used in any program that uses the ROSE library.
This library gathers and documents math code previously spread over the STEP Tools® libraries for STEP, IFC, and other engineering data and removes depencencies on specific EXPRESS schemas. The result contains definitions for the for mesh structures used by the STEP and IFC Faceter libraries. It also has a full range of vector arithmetic and coordinate system transform functions, unit conversion, and bounding box resources. It also has utilities for writing the mesh data to XML and JSON structures.
The STEP Faceter, IFC Faceter, and STEP helper function libraries now use the mesh, transform, bounding box, and unit data types provided by the ROSE Math library. As a result, you may need to change some symbols when updating code that used the earlier definitions.
General Updates
The Core SDK is stronger after stress tests with thousands of the most abusive files that Microsoft and our corporate customers could make. We are also updated for the recently published third edition of the STEP file format!
- ROSE Library [change log]
- The library uses the full directory path when checking if a file is already in memory. A program can now read both "dir1/foo.stp" and "dir2/foo.stp". Call ROSE.findDesign() and findDesignInWorkspace() with a full pathname for best results. The RoseDesign name() and path() functions also take a full file path now.
- Best-fit matching from EXPRESS to C++ classes now chooses a
complex instance combination for a subset of types if the full
combination is not available, and it now finds the class that covers
the most attributes or subtypes. Most best-fit circumstances came from
adding an extra type or subtype to a complex instance combo, which
will now be handled as a useful nearest combo rather than a
less-useful supertype.
- Added more functions for Part 21 Edition 3 references. In particular, you can now assign an object to a reference and propogate that to all usages. We are also annotating anchors with the type of their underlying object to help improve clarity in E3 files.
- Applications are now 5% smaller and have increased performance. Some functions non-virtual and removing ones that were never widely used or can be handled better in a different way. Minor API changes also simplify things and help with compiler checking. In particular, we made the return values for many string access functions const char rather than just char.
- New RoseDesign fileArchiveMember() holds the path within an archive, such as a zip file, that a design was read from or will be written to. If null, it will use the default name.
- New RoseTypesCursor class for traversing several disconnected types at once.
- The STEP file reader is has been tested against thousands of STEP files that were intentionally corrupted by Microsoft "fuzz" testing tools.
- The Part21 edition 3 test implementation has been exercised by vendor interoperability testing of the new anchors and URL references. We also sponsored the development of open source programs to split and merge P21 files using the P21e3 spec.
- When writing Part 21 files, no longer line wrapping within \X\ encoded hex escape sequences. Wrapping is legal, but some systems are not well-written and have trouble with that.
- Added enable()/disable() to error context for simpler turning on/off of individual messages. Error reporting respects ROSE_LOG instead of always using 'roselog'.
- Fixed crashes when renumbering EIDs on an empty design and when writing a null XML attribute.
- The rose_put_nested_object() and rose_create_select() functions now work properly with very deeply nested select types.
Supported Platforms
The STEP Tools® Development Stack is available for the operating systems and compiler combinations shown below. Contact us to arrange other configurations. Each platform has library versions for use with specific C++ compilers and build flags. See Windows Installation, MacOS Installation, and UNIX Installation for details on each.
| Platform | Supported Compilers |
|---|---|
| Windows 10/8/7 32bit | Visual Studio 2015 (VC++ 14), Visual Studio 2013 (VC++ 12), Visual Studio 2012 (VC++ 11), with the /MD option. Library versions for static and DLL linking. |
| Windows 10/8/7 64bit | Visual Studio 2015 (VC++ 14), Visual Studio 2013 (VC++ 12), Visual Studio 2012 (VC++ 11), with the /MD option. Library versions for static and DLL linking. |
| MacOS 10.12 (Sierra) to 10.9 (Mavericks) | Clang (Xcode 8.0) with libraries built for Mach-O universal binaries. Library versions for plain and position-independent static linking, and dynamic linking. |
| Linux 32bit All recent distros, RHEL 5, SuSE 10-11, and anything with glibc 2.5+. |
GCC 3.4/4.x. Library versions for plain and position-independent static linking, and dynamic linking. |
| Linux 64bit All recent distros, RHEL 5, SuSE 10-11, and anything with glibc 2.5+. |
GCC 3.4/4.x. Library versions for plain and position-independent static linking, and dynamic linking. |
| IBM POWER-series AIX v5.3, POWER5 |
IBM XL C/C++ 64bit. Library versions for plain and thread safe static linking. |
| Hewlett Packard HP-UX v11, Itanium |
HP ANSI C++ 64bit. Library versions for plain and position-independent static linking (+Z -z -mt) |
| Solaris v10+, SPARC | Sun Studio v11 64bit. Library versions for plain and position-independent static linking (-PIC -mt) |
| Solaris v10+, Intel x86 | Sun Studio v11 64bit. Library versions for plain and position-independent static linking (-PIC -mt) |